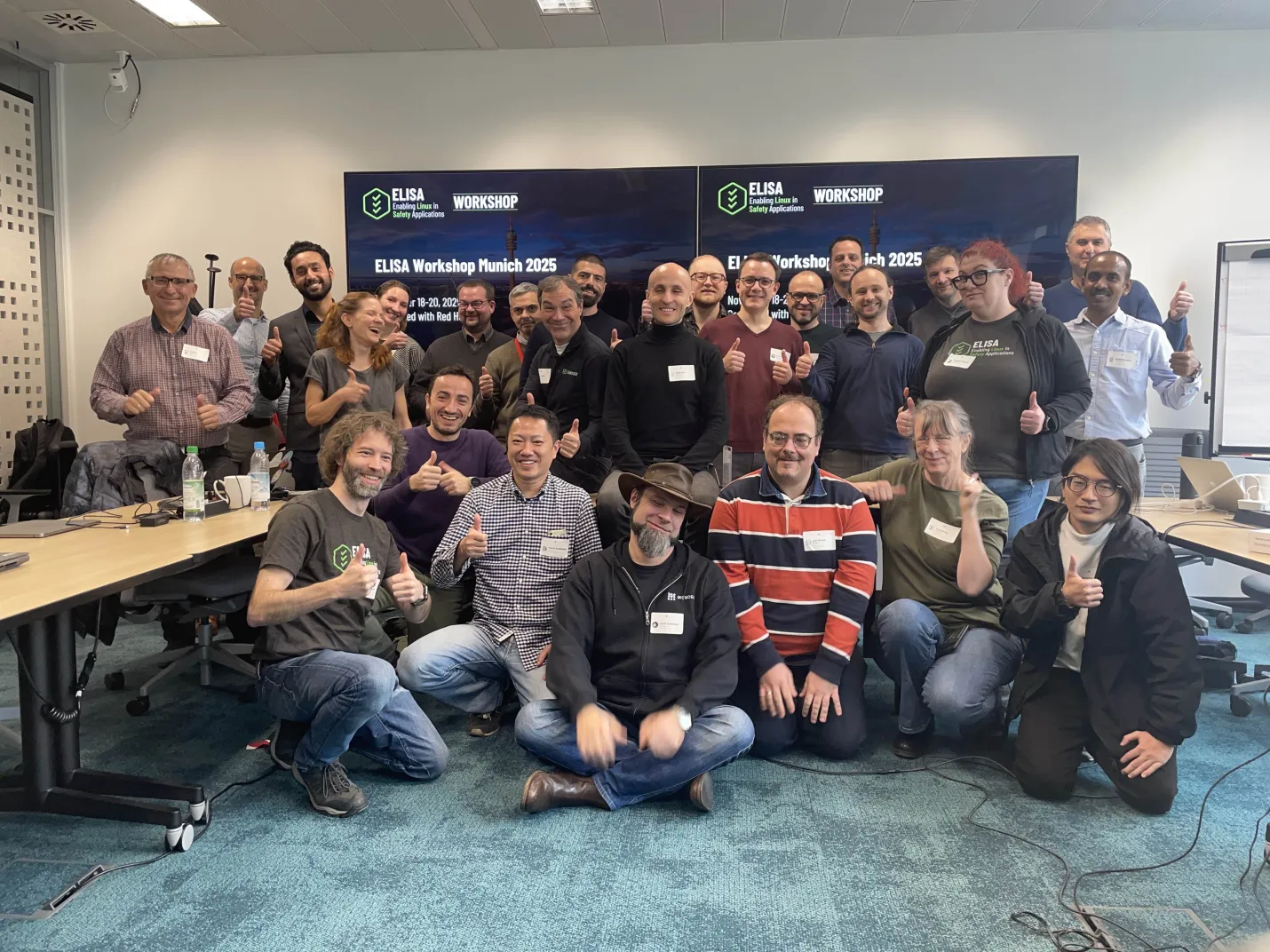
The ELISA Workshop Munich 2025 took place November 18-20 at the Red Hat office in Grasbrunn, Germany, bringing together project members, contributors, and industry partners for three days of focused collaboration.
Welcome & Introductions Gabriele Paoloni, Red Hat; Kate Stewart, Linux Foundation; Philipp Ahmann, ETAS GmbH
The ELISA Workshop opened with a welcome note from organizers who introduced logistics, guidelines, and expectations for collaboration, including the code of conduct and Chatham House Rule options. Participants from industry, academia, and open source communities briefly introduced themselves, reflecting a diverse range of expertise in safety-critical systems, Linux engineering, certification, and research.
Ask Me Anything – New Contributor Onboarding Gabriele Paoloni, Red Hat; Philipp Ahmann, ETAS GmbH
The “Ask Me Anything about ELISA or the Use of OSS in Safety-Critical Applications” session, led by Gabriele Paoloni and Philipp Ahmann, offered participants an open space to address foundational questions about applying Linux and open source software in safety-critical systems. The conversation clarified why live Q&A remains valuable beyond static FAQs, explored the challenges of using Linux in complex safety contexts, and outlined how ELISA approaches requirements, standards, tooling, and system understanding.
The session also highlighted common misconceptions such as the idea of producing a “safe Linux”and reinforced the importance of context, collaboration, and evolving industry practices when integrating OSS into safety-relevant applications.
Research questions and publication directions of Aerospace WG Martin Halle, Hamburg University of Technology – Institute of Aircraft Systems Engineering, Matthew Weber, Boeing
This session outlined key research questions for the Aerospace Working Group, focusing on where Linux is currently used in aerospace and space systems, how regulations affect its adoption, and which topics should lead to future white papers. The speakers also introduced shared use cases and tools supporting this work and invited contributors with domain expertise to help advance upcoming publications.
Towards Practical Program Verification for the Linux Kernel Keisuke NISHIMURA, Inria
The session “Towards Practical Program Verification for the Linux Kernel,” presented by Keisuke Nishimura, Jean-Pierre Lozi, and Julia Lawall, introduced foundational concepts of deductive program verification and demonstrated their application through a case study on the kernel function. The speakers highlighted challenges in specifying correct behavior, automating loop invariants, and preparing verification-ready code, and outlined research efforts aimed at making large-scale kernel verification more practical.
Towards a More Sustainable and Secure Software Tooling in Free/Libre Open Source Software Environments Stefan Tatschner, Fraunhofer AISEC
The session “Towards a More Sustainable and Secure Software Tooling in Free/Libre Open Source Software Environments”, presented by Dr. Stefan Tatschner (Fraunhofer AISEC), explored how software sustainability and security intersect in FLOSS ecosystems. Building on his PhD work, Dr. Tatschner discussed how vague or overly complex specifications and fragmented development practices can lead to inconsistent, insecure implementations, illustrated through studies of QUIC stacks and X.509 libraries. He showed how dependency analysis and graph-based metrics can help identify critical projects whose health has a disproportionate impact on the ecosystem.
Introducing SW Requirements in the Linux kernel development process: status and next steps Gabriele Paoloni, Red Hat; Kate Stewart, Linux Foundation; Chuck Wolber, Boeing
The session “Introducing SW Requirements in the Linux Kernel Development Process: Status and Next Steps”, presented by Gabriele Paoloni (Red Hat), Kate Stewart (Linux Foundation), and Chuck Wolber (Boeing), explored how to bring structured software requirements into the Linux kernel’s distributed, maintainer-driven development model. The speakers highlighted gaps in existing documentation and explained how missing explicit intent increases technical debt and complicates safety and certification work. They proposed testable, SPDX-based requirement annotations that live alongside the code to improve clarity, traceability, and review. The talk also summarized feedback from kernel maintainers and outlined ongoing experiments and next steps to refine the approach and drive broader adoption.
Exploring possibilities for integrating StrictDoc with ELISA’s requirements template approach for the Linux kernel Tobias Deiminger, Linutronix; Stanislav Pankevich, Reflex Aerospace
The session “Exploring Possibilities for Integrating StrictDoc with ELISA’s Requirements Template Approach for the Linux Kernel”, presented by Tobias Deiminger (Linutronix GmbH) and Stanislav Pankevich (Reflex Aerospace GmbH), demonstrated how the StrictDoc tool can support structured, traceable requirements workflows for kernel development. The speakers introduced StrictDoc’s capabilities, showed how it is already used at Linutronix for certification-driven projects, and walked through a live prototype integrating SPDX-based requirements directly from kernel source files. They highlighted how StrictDoc can link requirements, code, and tests while enabling validation and drift detection. The session emphasized that such tooling could strengthen documentation quality, improve traceability, and complement ELISA’s efforts to introduce maintainable requirements practices into the kernel ecosystem.
Architectures for Linux in Railway Safety Applications Florian Wühr, Red Hat; Daniel Weingaertner, Red Hat
The session “Architectures for Linux in Railway Safety Applications”, presented by Florian Wühr and Dr. Daniel Weingärtner (Senior Software Engineers, Red Hat EMEA Field CTO Office), explored how Linux-based platforms can be used in modern railway safety systems. They outlined Red Hat’s involvement in the “AutomatedTrain” research project and discussed applying high-performance, Linux-based platforms for autonomous and safety-related rail use cases. The talk covered relevant safety standards and SIL levels, key certification and interoperability challenges in Europe, and compared architectural options (containers, hypervisors, redundancy/diversity) for mixed-criticality railway applications.
Hypervisors are scary, so why use them for enabling Linux for Safety Applications Aqib Javaid, Elektrobit
The session explained why hypervisors, though often viewed as complex or risky, are valuable for enabling Linux in safety-critical systems. Aqib Javaid clarified common misconceptions such as hypervisors being slow or unusable for safety and showed how modern hardware support and open-source options like Xen and L4 make them practical and certifiable. He demonstrated how hypervisors provide strong isolation and allow a small safety monitor to supervise Linux, adding protection without modifying the kernel.
Open Functional Safety: Safety-Qualified Lifecycle with Sphinx Christopher Zimmer, innotec GmbH
The session “Open Functional Safety: Safety-Qualified Lifecycle with Sphinx” was presented by Christopher Zimmer (innotec GmbH). He showed how an open-source toolchain centered on Sphinx can support a full, safety-qualified development lifecycle for smaller companies and open source projects that can’t afford heavy commercial tooling. The talk also outlined how to classify and qualify such tools so they can be used in standards-compliant functional safety workflows.
AGL SDV SoDeV Insights Naoto Yamaguchi, AISIN; Harunobu Kurokawa, Renesas
The session “AGL SDV SoDeV Insights,” presented by Naoto Yamaguchi (AISIN) and Harunobu Kurokawa (Renesas), shared progress on Automotive Grade Linux’s Software-Defined Vehicle initiative. The speakers outlined SoDeV’s goal of decoupling hardware and software using open-source technologies like hypervisors, VirtIO, and unified HMI frameworks to enable reusable, scalable in-vehicle software. They also discussed early prototypes, planned architecture, and open challenges particularly around safety and integrating monitoring in virtualized systems.
Best Practices in Open Source and Standards – Evaluation of Example Projects Simone Weiss, Linutronix
The session presented work from ELISA’s WG Lighthouse OSS on identifying open-source “best practices” and mapping them to quality/safety standards. Simone showed how a common evaluation template was applied to Xen and Yocto, revealing both strong governance/CI practices and recurring issues like fragmented documentation, and outlined plans for a maturity model to rate project process quality.
Beyond the OS: What else is required for safe automotive applications? Isaac Trefz, Elektrobit
The session “Beyond the OS: What Else Is Required for Safe Automotive Applications?” highlighted that making Linux safe is only one part of building a safety-compliant automotive system. Isaac Trefz (Elektrobit) explained that safe applications also require qualified compilers and libraries, safe IPC, reliable rendering paths, hypervisors, hardware support, and proper monitoring/watchdog mechanisms. Using examples like telltales and ADAS functions, he showed how these system-level elements must work together.
BASIL Luigi Pellecchia, Red Hat
The session “BASIL,” presented by Luigi Pellecchia (Red Hat), introduced BASIL as a tool for managing traceability across requirements, code, and tests in safety-critical projects. Luigi highlighted recent updates improved SPDX SBOM export, graphical traceability views, expanded test-framework support, and a new AI-assisted requirement generator. He also outlined a proposal for a configurable traceability scanner that pulls structured data from multiple repositories, aiming to simplify and standardize traceability workflows in open-source safety development.
Continuous Compliance in Safety-Critical Open Source Projects Rinat Shagisultanov, InfoMagnus
The session “Continuous Compliance in Safety-Critical Open Source Projects,” presented by Rinat Shagisultanov (InfoMagnus), showed how safety-annotated SBOMs—using SPDX 3 and its emerging safety profile can automate functional-safety traceability. Rinat explained how tools like BASIL generate these SBOMs and how the OpenCC platform performs semantic diffs, impact analysis, and audit logging inside CI/CD pipelines.
Industry Safety Level(s) vs. Aerospace Use Cases Matthew Weber, Boeing
The session “Industry Safety Level(s) vs. Aerospace Use Cases,” presented by Matthew Weber (Boeing), explained how civil aerospace develops and certifies aircraft software using DO-178C safety levels (DAL A–E), and how these compare conceptually to ASIL/SIL levels in other industries. He walked through the aircraft lifecycle, showed how safety levels drive required artifacts and rigor, and illustrated everything with example use cases and early Linux-based demos (like a safety-aware “cabin light” and NASA CFS-based scenarios).
Linux Virtual Address Space Safety Alessandro Carminati, Red Hat
The session “Linux Virtual Address Space Safety,” presented by Alessandro Carminati (Red Hat), explored how Linux’s virtual memory design especially Virtual Memory Areas (VMAs) and the global linear mapping creates subtle safety risks in mixed-criticality systems. He walked through the VMA lifecycle, showed how the linear map lets kernel and user pages sit side-by-side (enabling accidental cross-domain corruption), and reviewed current defenses and why they’re aimed at security/debugging rather than deterministic functional safety.
Behind the Scenes: Elisa Yocto meta-layer and the ELISA CI infrastructure Sudip Mukherjee, Codethink
The session “Behind the Scenes: ELISA Yocto Meta-Layer and the ELISA CI Infrastructure,” presented by Sudip Mukherjee (Codethink), gave a concise behind-the-scenes look at how ELISA’s Yocto meta-layer and CI system are built and maintained. Sudip explained how the team created a standardized Docker-based build environment, added nightly CI builds, shared sstate caching, and automated testing with QEMU and OpenQA. He also highlighted ongoing work to keep the AGL-based demo app building reliably and invited other working groups to adopt the shared CI to ensure reproducible, stable builds.
The SPDX Safety Profile Release Candidate – towards standardised safety supply chain documentation Nicole Pappler, AlektoMetis
The session “The SPDX Safety Profile Release Candidate – Towards Standardised Safety Supply Chain Documentation” by Nicole Pappler (AlektoMetis) presented the new SPDX 3.1 safety profile, which extends the core SPDX model with safety-specific concepts like requirements, verifications, and evidence links. Nicole explained how this enables standardized, machine-readable safety documentation across the software supply chain, improving traceability, impact analysis, and compliance for safety-critical industries using open source.
Drawing an open source safety-critical landscape Philipp Ahmann, ETAS GmbH
The session “Drawing an Open Source Safety-Critical Landscape” by Philipp Ahmann (ETAS) outlined the need for a clear map of the growing ecosystem of safety-critical open source projects. Philipp proposed building a structured landscape covering OSs, hypervisors, tools, frameworks, simulators, and industry domains to show how projects relate, where they fit, and where gaps or collaboration opportunities exist. The goal is to give the community a central, easy-to-navigate view of safety-critical open source efforts.
In short:
The Munich workshop highlighted the rapid progress and growing cohesion of the safety-critical open source ecosystem. Over three days, contributors shared tools, research, architectures, requirements approaches, and CI practices all reinforcing that using Linux in regulated environments requires aligned methods, clear documentation, traceability, and strong cross-community collaboration.
With active participation from industry, academia, and open-source projects, the workshop wrapped up with renewed momentum and a shared commitment to push ELISA’s technical work forward.
Note: Presentation Slides can be accessed here
Would like to see the photos from the meetup? Check here.
Check the workshop playlist in the ELISA YouTube.
Interested to host the next ELISA workshop?
The ELISA Project hosts workshops on a regular basis to gather the project community to accelerate technical collaboration and output, and plan for future goals. It is intended as a technical community collaboration forum to advance the mission of the ELISA Project. More specifically, the Workshop series provide the avenue to:
- Explore ideas about approaches, processes, tooling, and testing that can be incorporated into building safety-critical applications and systems
- Exchange perspectives and feedback from the Linux kernel, safety, and other adjacent open source project communities
- Provide updates about the various Working Groups’ current activities and priorities and future roadmaps
- Enable real-time collaboration to make more accelerated progress on current work streams
- Define and articulate near-term technical goals and priorities
- Educate and onboard new community members
- Activate and increase engagement and contributions from a broader range of contributors
- The workshops are generally held in person to facilitate more open discussions and real-time collaboration. Virtual access can be provided if there is sufficient interest.
Contact us to discuss hosting a workshop.